Polynomials.solution
EXERCISE 2.2
(α+β)2=α2+β2+(2αβ)
16r2=24+2×4r
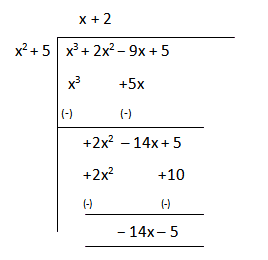
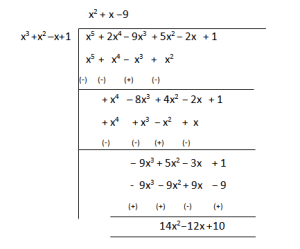
EXERCISE 2.2
Q.1 Find the zeroes of the following quadratic polynomials and verify the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients.
(i) 6x² + 11x + 5 = 0
Soln: –
6x2 + 11x + 5 = 6x2 + 6x + 5x + 5
= 6x(x +1) + 5(x +1)
= (x +1) (6x +5)
∴ zeroes of polynomial equation 6x2 +11x +5 are { −1, −56 }
Now, Sum of zeroes of this given polynomial equation = −1+( −56 ) = −116
But, the Sum of zeroes of any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = −coeff.ofxcoeff.ofx2
= −116
And Product of these zeroes will be = −1×−56 = 56
But, the Product of zeroes of any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = constanttermcoeff.ofx2
= 56
Hence the relationship is verified.
(ii) 4s2 – 4s + 1
Sol:
4s2 – 4s + 1 = 4s2 – 2s – 2s + 1
= 2s (2s – 1) –1(2s – 1)
= (2s – 1) (2s – 1)
∴ zeroes of the given polynomial are: {12,12 }
∴ Sum of these zeroes will be = = 1.
But, The Sum of zeroes of any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = −coeff.ofscoeff.ofs2
= −44 = 1
And the Product of these zeroes will be = 12×12
=14
=
But, Product of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = constanttermcoeff.ofs2
= 14 .
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(iii) 6x2 – 3 – 7x
Sol:
6x2 – 7x – 3 = 6x2 – 9x + 2x – 3
= 3x (2x – 3) +1(2x – 3)
= (3x + 1) (2x – 3)
∴ zeroes of the given polynomial are: – (−13,32 )
∴ sum of these zeroes will be = −13+32
=76
=
But, The Sum of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = −coeff.ofxcoeff.ofx2
= 76
And Product of these zeroes will be = −13×32=−12
Also, the Product of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by =constanttermcoeff.ofx2
Also, the Product of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by =
= −36 = −12
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(iv) 4u2 + 8u
Sol:
4u2 + 8u = 4u (u+2)
Clearly, for finding the zeroes of the above quadratic polynomial equation either: – 4u=0 or u+2=0
Hence, the zeroes of the above polynomial equation will be (0, −2)
∴ Sum of these zeroes will be = −2
But, the Sum of the zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = −coeff.ofucoeff.ofu2
= −84 = −2
And product of these zeroes will be = 0 × −2 = 0
But, the product of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = constanttermcoeff.ofu2 = −04 = 0
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(v) t2 – 15
Sol:
t2 – 15 = (t+ 15−−√ ) (t − 15−−√ )
Therefore, zeroes of the given polynomial are: – {15−−√ , −15−−√ }
∴ sum of these zeroes will be = 15−−√ − 15−−√ = 0
But, the Sum of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = −coeff.ofxcoeff.ofx2
= −01 = 0
And the product of these zeroes will be = (15−−√ ) × (−15−−√) = −15
But, the product of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by
= constanttermcoeff.oft2 = −151 = −15
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(vi) 3x2 – x – 4
Sol:
3x2 − x − 4 = 3x2 – 4x + 3x − 4
= x (3x – 4) +1(3x – 4)
= ( x + 1) (3x – 4)
∴ zeroes of the given polynomial are: – {−1, 43 }
∴ sum of these zeroes will be = −1 +43 = 13
But, the Sum of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = −coeff.ofxcoeff.ofx2
= −(−1)3 = 13
And the Product of these zeroes will be = {−1 × 43 }
= −43
But, the Product of zeroes in any quadratic polynomial equation is given by = constanttermcoeff.ofx2
= −43
Hence, the relationship is verified.
Q2. Form a quadratic polynomial each with the given numbers as the sum and product of its zeroes respectively.
(i). 26 , −3
Sol.
Given,
α + β = 26
αβ = −3
∴ If α and β are zeroes of any quadratic polynomial, then the quadratic polynomial equation can be written directly as:-
x2 – (α+β)x +αβ = 0
Thus, the required quadratic equation will be:
x2 – (26 )x −3 = 0
6x2 − 2x – 18 = 0.
(ii). 3–√ , 43
Sol.
Given,
α + β = 3–√
αβ = 43
∴ If α and β are zeroes of any quadratic polynomial, then the quadratic polynomial equation can be written directly as: –
x2 – (α+β)x +αβ=0
Thus, the required quadratic equation will be: –
x2 – (3–√ )x + 43 =0
3x2 − 33–√x + 4 = 0.
(iii). 0, 7–√
Sol.
Given,
α + β = 0
αβ = 7–√
∴ If α and β are zeroes of any quadratic polynomial, then the quadratic polynomial equation can be written directly as:-
x2 – (α+β)x +αβ=0
Thus, the required quadratic equation will be: –
x2 – (0)x + 7–√ = 0
x2 + 7–√ = 0.
(iv). −2, −2
Sol.
Given,
α + β = −2
αβ = −2
∴ If α and β are zeroes of any quadratic polynomial, then the quadratic polynomial equation can be written directly as:
x2 – (α+β)x +αβ=0
∴ The required quadratic polynomial will be:
x2 – (−2)x −2 = 0
x2 + 2x – 2 = 0.
(v). −72 , 39
Sol.
Given,
α + β = −72
αβ = 39
∴ If α and β are zeroes of any quadratic polynomial, then the quadratic polynomial equation can be written directly as: –
x2 – (α+β)x +αβ = 0
∴ The required quadratic polynomial will be:
x2 – (−72 )x + 39 = 0
18x2 + 63x + 6 = 0.
(vi). 6, 0
Sol.
Given,
α + β = 6
αβ = 0
∴ If α and β are zeroes of any quadratic polynomial, then the quadratic polynomial equation can be written directly as:-
x2 – (α+β)x +αβ = 0
∴ The required quadratic polynomial will be:-
x2 – 6x + 0 = 0
x2 – 6x = 0.
EXTRA QUESTIONS
Q.1 Find a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are: -2+12√ , 2−12√ .
Sol.
Given: –
α + β = 2+12√ + 2−12√
= 4.
αβ = (2+12√)(2−12√)=4−12=72
∴ If α and β are zeroes of any quadratic polynomial, then the quadratic polynomial equation can be written directly as: –
x2 – (α+β)x +αβ = 0
Thus, the required quadratic polynomial equation will be :-
x2 – (4)x −72 = 0
2x2−8x+7 = 0.
Q.2 If α and β are the roots of a quadratic polynomial ax2+bx+c, then find the value of α2 + β2.
Sol.
From the equation, (α+β=−ba)
And, α×β=ca
∴ α2+β2=(α+β)2−2αβ
∴ α2+β2=(−ba)2−2ca
∴ α2+β2=b2a2−2ca
∴α2+β2=b2−2aca2 .
Similarly, we can find out the values of (α3 + β3) and (α3 – β3).
Q3. If α and β are zeroes of a quadratic polynomial x2+4x+3, form the polynomial whose zeroes are 1+αβand1+βα .
Sol.
Since α and β are zeroes of a quadratic polynomial x2+4x+3,
α+β= -4, αβ = 3
Given: – α1 = 1+αβ
β1 = 1−βα
Now, sum of zeroes = 1+αβ+1+βα
= 2+αβ+βα
= 2αβ+α2+β2αβ
= (α+β)2αβ
On putting values of α+β and αβ from above we get:-
Sum of zeroes = α1 + β1 = −423
= 163
Now, Product of zeroes = (1+αβ)(1+βα)
=1+βα+αβ+αββα
=2αβ+β2+α2αβ
= (α+β)2αβ
On putting values of α+β and αβ we get:
Product of zeroes = α1 × β1 = −423
= 163
Thus the required quadratic polynomial equation will be:-
x2 – (α1 + β1)x + α1β1 = 0
x2 – (163 )x + 163 = 0
3x2 – 16x +16=0.
Q4. If α and β are zeroes of a quadratic polynomial p(x) = rx2+4x+4, Find the values of “r” if: – α2 + β2 = 24.
Sol.
From the given polynomial p(x),
α + β = −4r , and αβ = −4r ………. (1)
Since,(α + β)2 = α2 + β2 + 2αβ
Given, α2 + β2 = 24 and from equation (1).
Therefore, (−4r)2=24+2×4r
16 = 24 r2 + 8r
3r2 + r – 2 = 0
3r2 + 3r – 2r -2 = 0
3r(r+1) – 2(r+1) = 0
(3r-2) (r+1) = 0
∴ r = 23 or r = -1
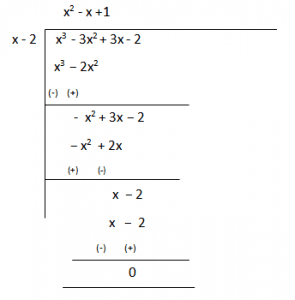
EXERCISE 2.3
Q.1 If a polynomial x3 -3x2+x+2 is divided by a polynomial g(x), the quotient and remainder obtained are (x-2) and (-2x+4), respectively. Find the equation of g(x).
Sol.
Since, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
Therefore, x³ -3x2+x+2 = g(x) × (x-2) + (-2x+4)
(x3 -3x2+x+2) – (-2x+4) = g(x) × (x-2)
Therefore, g(x) × (x-2) = x3 -3x2+3x-2
Now, for finding g(x) we will divide “x3 -3x2+3x-2” with (x-2)
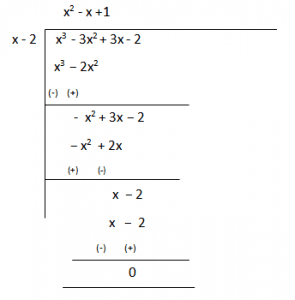
Therefore, g(x) = (x2 – x +1)
Q.2 Find the quotient and remainder by dividing the polynomial f(x) by the polynomial g(x).
(i) f(x) = x3 + 2x2 – 9x + 5, g(x) = x2+5
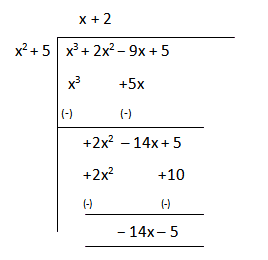
Therefore, Quotient is (x+2) and Remainder is (-14x − 5)
(ii) f(x) = x5+2x4-9x3+5x2-2x+1, g(x) = x3 + x2 – x+1
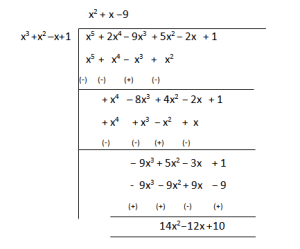
Therefore, Quotient is (x2 + x − 9) and Remainder is (14x2 – 12x +10)
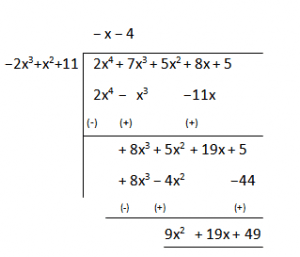
(iii) f(x) = 2x4 + 7x3 + 5x2 + 8x + 5, g(x) = 11− 2x3 + x2
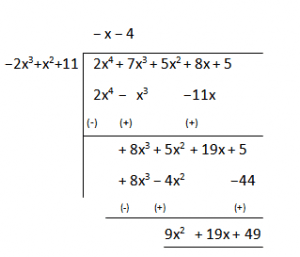
Therefore, Quotient is – (x + 4) and Remainder is (9x2 + 19x +49).
2–√and−2–√ are zeroes of f(x).
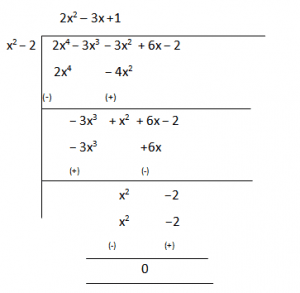
2–√,−2–√,12and1 .
Q3. Find all the zeroes of the polynomial equation 2x4-3x3-3x2+6x-2, if two of its zeroes are 2–√and−2–√ .
Sol.
Since this is a polynomial equation of degree 4, there will be a total of 4 roots.
Let, f(x) = 2x4 – 3x3 – 3x2 + 6x – 2
∴(x−2–√)(x+2–√) = (x2− 2) = g(x), is a factor of given polynomial f(x).
If we divide f(x) by g(x), the quotient will also be a factor of f(x) with remainder =0.
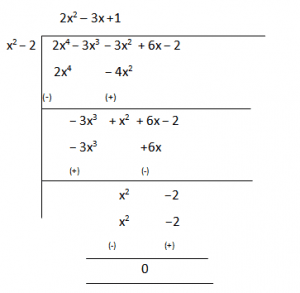
So, 2x4 − 3x3 − 3x2 + 6x – 2 = (x2 – 2) (2x2 – 3x +1).
Now, on further factorizing (2x2 – 3x +1) we get,
2x2 – 3x +1 = 2x2 – 2x − x +1 = 0
2x (x − 1) – 1(x−1) = 0
(2x−1) (x−1) = 0
So, its zeroes are given by: x= 12 and x = 1
Therefore, all four zeroes of the given polynomial equation are:
No comments:
Post a Comment